An orientation to Refraction Chamber
Introduction
Refraction chamber is very essential in eye care practice for doing preliminary vision assessment of all patients and also to know the impact of their diseases/disorders. A refraction chamber is a technical unit, a semi-dark room 3 or 6 metres in length and 1½ metres in width. Refraction evaluation is done to prescribe suitable glasses for correcting the patient’s vision problems, and for carrying out individualised visual needs in terms of subjective and objective refraction.
Equipments Needed in Refraction Chamber
General Equipment
- Plane mirror to reflect the Snellen’s chart letters
- Adjustable illumination set for variable light conditions mainly for near vision assessment
- Torch for doing the preliminary examination
Clinical Equipment
- Trial frame and standard trial lens set / phoropter
- Streak retinoscope
- Snellen’s vision drum / chart projector
- Near vision chart
- Auto refractometer
- Accessory lenses: Occluder, Pinhole disc, JCC, Maddox rod, Stenopic slit and Red and Green and prism lenses
- Prism bar
- PD ruler
- RAF Ruler
- Color vision chart
- Topical drugs - mydriatic and cycloplegic agents
- Lensometer
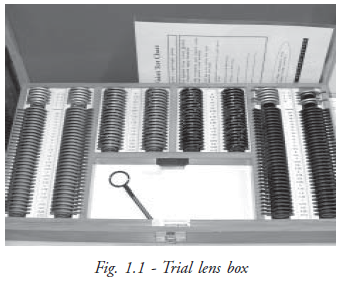
Trail Lens Box : Trial lens set is the primary and most essential device in a refraction chamber (Fig. 1.1). A standard trial lens set contains a pair of plus and minus lenses on each power in sphere and cylinder form. The spherical lenses are available in the ranges from 0.12 D to 20.0 D and the cylindrical lenses from 0.12 D to 6.0 D. The accessory lenses are occluder, pinhole disc, stenopic slit, Maddox rod, Red and Green goggles and prisms from 0.5 to 12.0 D are also available in the trial set. All trial lenses are mounted either by a metal or plastic rim with hand grip for easy handling. In cylindrical lens, axis meridian is indicated by special marks and comes without handle for easy rotation. Prism has its apex and base marked on the lens.
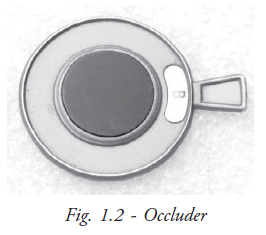
Occluder Occluder is an opaque disc used to close or cover one eye during refraction examination (Fig. 1.2). It blocks one eye vision while performing the test on the fellow eye, so that we can check each eye separately. In occluder, the opaque disc is mounted either in metal or plastic rim with hand grip for easy handling.
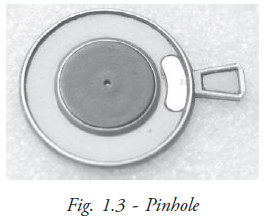
Pinhole: Pinhole is an opaque disc used for determining whether the decreased vision is due to refractive error or due to pathological diseases of the eye (Fig. 1.3). It actually reduces the retinal blur and allows the central light rays to reach the macula (retina) which enhances vision. Pin holes are available in the ranges of 1mm, 2mm in diameters. The optimum size of 1.32 mm is recommended as a standard one. Multiple pinholes are a better option if patient is not able to view through the visual axis and for patients with low vision.
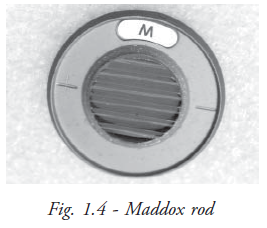
Maddox rod: Maddox rod is constructed of a series of red cylindrical rods (Fig. 1.4). Each rod acts as a strong ‘+’ cylindrical lens that forms a red streak band before the eye. It is used to detect the presence of heterophoria and to measure the amount of heterotropia.
Stenopic slit : It consists of a rectangular aperture with a linear slit 1mm in width and up to 15 mm in length (Fig. 1.5). It is useful for refining the axis of high irregular astigmatism.

Red and Green filters: Red and green goggles are mainly used in checking the binocular single vision by worth’s four dot test and stereopsis test using TNO charts.
Jackson Cross Cylinder (JCC): JCC is a combination of minus and plus cylinder power, the same power located perpendicular to each other and supported with hand grip (Fig. 1.6). The axis of two cylinders is marked in white and red colors. The white mark indicates the axis of ‘+’ cyl and the red indicates the axis ‘-’ cyl. It is used for determining the power and for refining the correct axis. Cross cylinders are available in 0.12D, 0.25D, 0.50D and 1.0D powers.

Trial frame: The trial frame is a metallic / plastic frame for holding the trial lenses before the eye during refraction (Fig. 1.7). Each eye frame is constructed of three cells on front side and one on back side. The front three surfaces of the trial frame are used for keeping the spherical, cylinder and other accessories i.e. occluder, pinhole etc. The second front cell is arranged for placing the cylindrical lens and the axis is marked counterclockwise. The extreme forward cell is molded with three knobs with support to place the lens accessories.
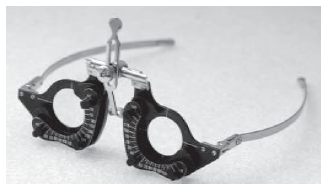
Like spectacles, two eye frames are being mounted by an adjustable bridge and sides. It is necessary to adjust the trial frame depending on the patient’s pupillary distance before starting the refraction test. Special trial frames are available for children and for doing low vision refraction.
Retinoscope: Retinoscope is one of the most essential tool for determining the patient’s refractive status objectively (Fig. 1.8). Retinoscope is the only device to estimate the refractive errors of those who are unable to co-operate, particularly children and mentally retarded persons.
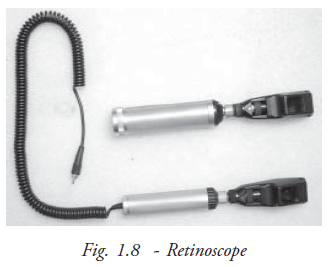
Retinoscope is basically available in two types. They are spot retinoscope and streak retinoscope. In the early days, the spot retinoscope was used widely and now the streak retinoscope is popular among the practitioners because of its simple and easy principles.
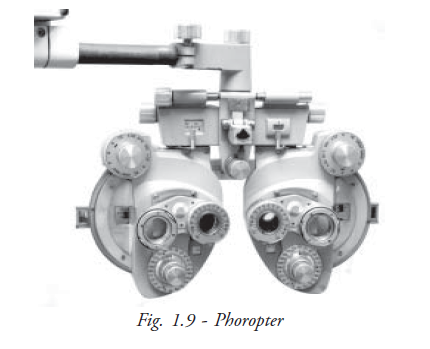
Phoropter: Phoropter or refractor is exclusively designed for refraction (Fig. 1.9). It is comprised of spherical lens, cylindrical lens, prisms and all types of auxiliary lenses. It is also equipped with Jackson cross cylinder. Although the trial lens/frame is used widely, a phoropter is capable of doing all the tests such as JCC test, duochrome test, measurement of phoria and tropia and the binocular vision test.
Auto refractometer: Auto refractometer represent the most advance technology of measuring the refractive powers of the eye. It is easily operated even by non technical persons (Fig. 1.10). It provides a quick reliable guideline for the objective refraction.

Colour vision: Ishihara color vision plates are used for screening for color blindness. This chart helps to detect red and green color deficiencies. It contains 38 plates includes 25 numerals plates and 13 pathway plates.
Lensmeter: The procedure used to measure the corrective lens powers i.e. sphere, cylinder and axis and prism or the power of rigid contact lenses is called lensometry. It is performed with a specialized instrument known as lensmeter or focimeter.
PD ruler scale: The interpupillary distance is measured using a PD ruler. Interpupillary distance is the distance between the center of pupils in millimeters. This measurement should be obtained for both near and distance for each patient.
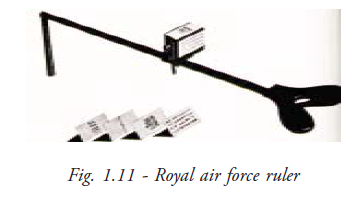
RAF ruler: RAF ruler is the instrument used for measuring the ability of accommodation and convergence (Fig. 1.11). It also provides the dioptric value of accommodation and convergence of the patient.
Prism bar: There are two prism bars in a box. One is for measuring horizontal deviation, the other for vertical deviation (Fig. 1.12). These bars are used for finding the fusional range.
Topical drugs
Mydriatics
Mydriatics causes the pupils to dilate, usually by stimulating the iris dilator muscle. It is used to facilitate the retinoscopy to the patients having opacity of visual axis and for funduscopy.
Cycloplegics
These drugs essentially paralyze the iris sphincter muscle causing dilation of the pupil. These agents also limit or prevent accommodation by paralysing the ciliary muscle, which controls the ability of the lens to expand and contract. Cycloplegic refraction is especially important in children, who have a strong accommodative mechanism that frequently interferes with accurate refraction.
Furniture
Standard furniture aids in refraction testing for obtaining the result very quickly. The movable revolving chairs may be a better option to the practitioners so that they can easily approach the patient. For the patient, a sophisticated chair for comfortable seating may be provided.
Cubicle Dimension and Space Management in Refraction Unit
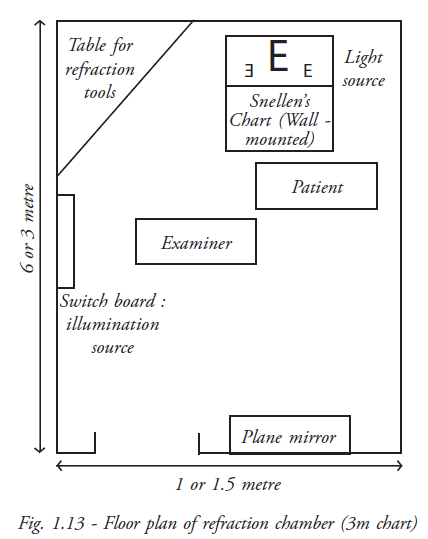
Normally the refraction room is arranged in a adequately long compartment with a dark environment because vision assessment is being done at a distance of 6 metres. Alternatively it can be planned in 3 metres distance by using a reversible letters on a chart that is reflected through a mirror towards the patient’s view.
Generally the refraction room may be arranged in a more spacious place to examine the patient as well as provide accommodation to the patient’s attendants. According to the space availability, plan the refraction cabin. Now many institutes prefer to have a 3 metre testing distance unit because of limited space. The following diagram illustrates the measurements and how to set a refraction testing room in three metres testing method.
Arrangements
The refraction room arrangements and location of the furniture should facilitate the examination as well as make the patient comfortable .Patient is seated to the right side of the examiner for easy approach.
Snellen’s drum is positioned straight over the patient’s head and the mirror placed straight in front of the drum at 3 metres so that all letters can be seen clearly in the patient’s normal viewing.
The adjustable illumination set is fixed by the side of the patient for near vision assessment. This can be adjusted while doing retinoscopy. The illumination level required is 19 foot candles (60W filament bulb which are equal to normal sunlight condition). For the proper illumination of the refraction room and air circulation standard electrical fittings are essential. The controlling switches should be located near the examiner for easy operation. Similarly assessment record forms / glass prescriptions forms are to be kept near the examiner.
Summary
In this unit we have covered the refraction room set up with all the necessary equipment. The length and breadth of the room, the lighting arrangement and the furniture details are also given. Details about the equipment with their uses will help the student identify the equipment and use it appropriately.
Key points to remember
- Vision assessment is a major tool in knowing the impact of diseases / disorders
- Refraction is an essential assessment in restoring the potential vision by optical correction
- Well - furnished refraction rooms facilitate comfortable refraction to both the patient and the practitioner
Student exercise
Answer the following
- Where will the trial set be kept?
- What is the distance between the drum (chart) and mirror?
- What is the diameter of the hole in the streak retinoscope?
- What is the diameter of the pinhole?
- What is the use of the pinhole?
- What are the uses of red and green glass?
- Describe about the arrangements in the trial frame
- What is a retinoscope?
- Mention the tests that could be done with phoropter
- Give a short note on refraction cubicle
